HTML elements can be classified into two categories:
- Semantic Elements
- Non-Semantic Elements
Semantic Elements
Semantic elements clearly show their purpose in the code and what content they hold. They make your web page more organized and have these benefits:
- Accessibility: Tools like screen readers can better understand and describe the content for users.
- SEO: Search engines can easily figure out your content and rank it higher.
- Readability: Your code is easier to understand and maintain for developers.
Examples of semantic elements: <header>, <footer>, <article>, <nav>, <section>
Non-Semantic Elements
Non-semantic elements don’t provide clear information about the content they hold. They are general-purpose containers, which can be styled or manipulated, but don’t indicate their purpose.
Examples of non-semantic elements: <div>, <span>
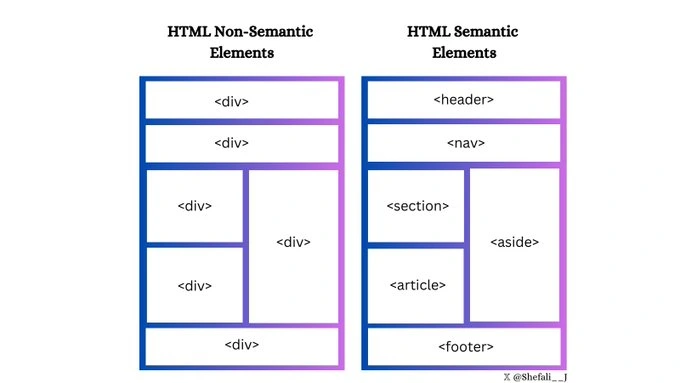
Why Choose Semantic Elements over Non-Semantic Elements?
- Clear Purpose: Semantic tags clearly show their role, making the code easier to understand.
- Enhanced Accessibility: Tools like screen readers can interpret the content more effectively.
- SEO Benefits: Search engines prioritize structured and meaningful content.
- Ease of Collaboration: Semantic tags make it simpler for other developers to collaborate on the codebase.
👉 Next tutorial: HTML Attributes